Beauty
Nine-to-five girlies are bonding over their shared experience of dry skin, frizzy hair, and melted makeup.
Drowsily, you apply makeup and spray dry shampoo at the roots before commuting to the office.
As lunchtime approaches, you steal a quick glance at your reflection.
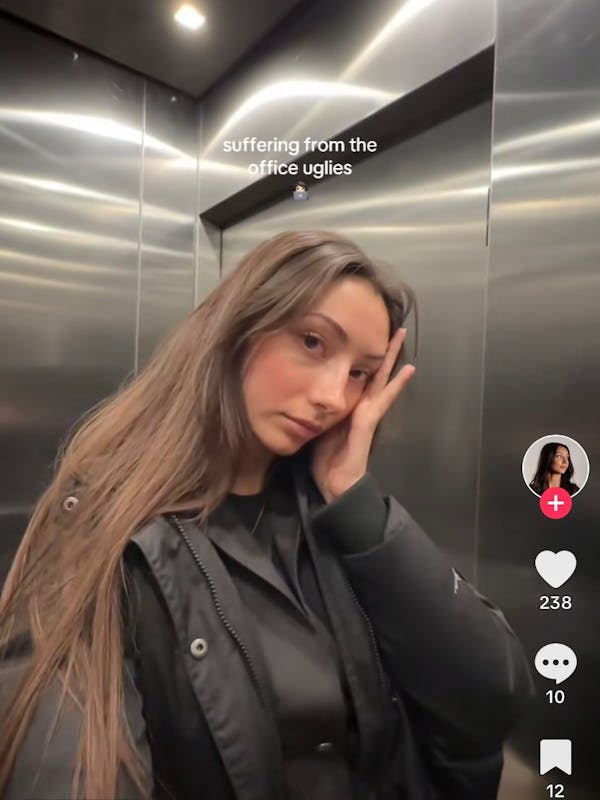
Have I looked like this all morning?
According to TikTok, this experience is shared by many and its all thanks to the office air phenomenon.
The Office Air Dilemma
The theory?
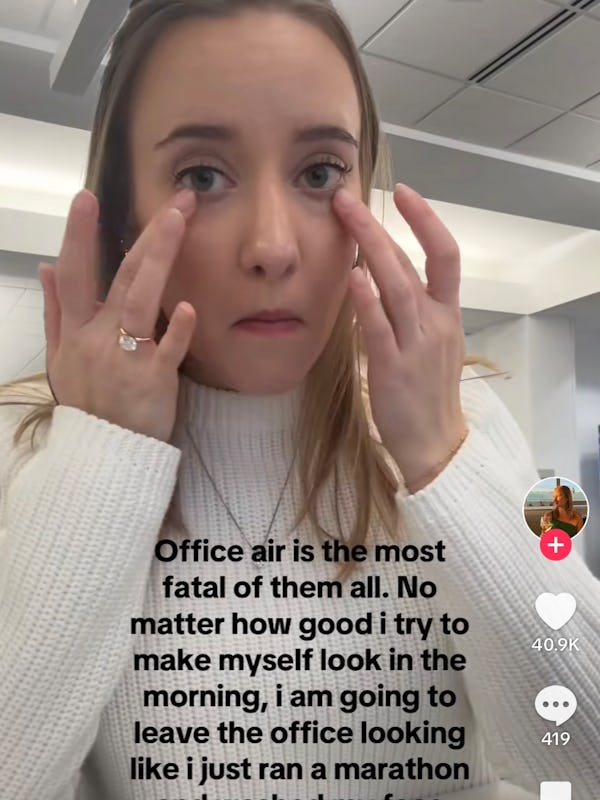
Something in the workplace environment negatively affects makeup system and overall appearance.
Whatever the case, nine-to-five girliesare humorously bondingover their shared experience of the office air dilemma.
Others have even provided step-by-step office air-proof makeup looks to lessen the damage.
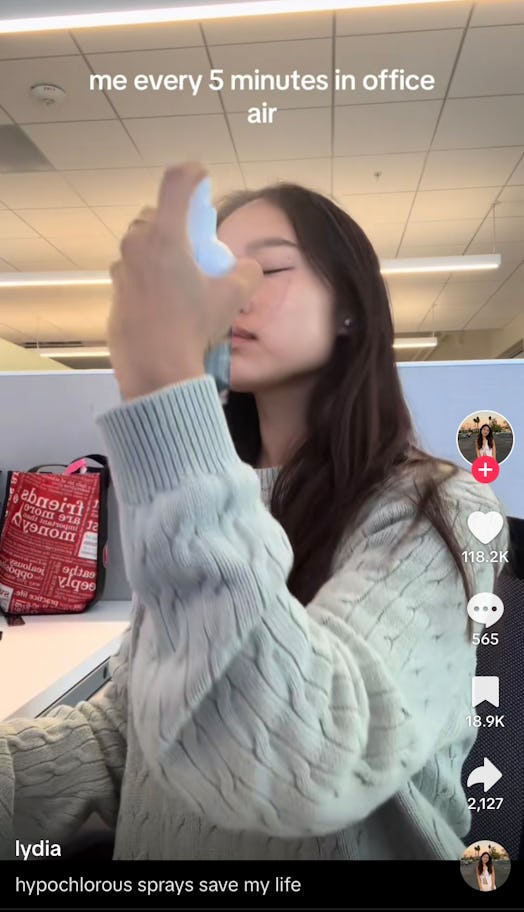
Something Is In The Air
According toDr.
Why might this be the case?
Thisleads to moisture loss in the skin and hair, contributing to overall dryness.
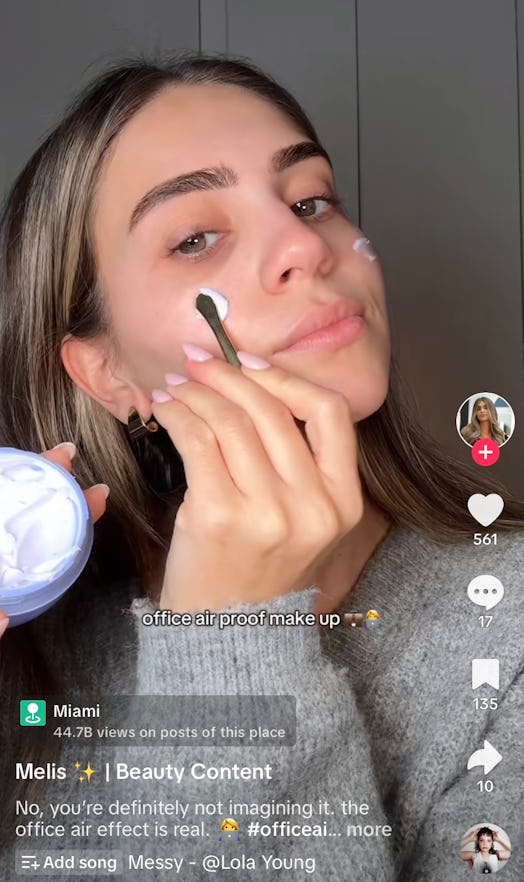
Plus, despite being indoors, your complexion isnt safe from sun damage when youre at work.
She shares that repeated exposure to these office conditions can lead to various physical signs.
Lips and hands can be particularly prone to dehydration, leading to chapping, she says.
Enduring long, demanding hours and inadequate sleep can manifest as visible signs on the exterior.
Combatting Workplace Uglies
Your first anti-office air tool is all about proper skin care.
The quickest way for your makeup to break down or deteriorate is in dry air environments, she says.
(2016).The effect of environmental humidity and temperature on skin barrier function and dermatitis.
J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol.
2016 Feb;30(2):223-49. doi: 10.1111/jdv.13301.
Epub 2015 Oct 8.
Farran, L. (2009).
Tensile and shear properties of fingernails as a function of a changing humidity environment.
Journal of Biomechanics.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiomech.2009.03.020
Gouin J-P. (2011).Chronic Stress, Immune Dysregulation, and Health.
American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine.
2010 Sep 23;5:277-84.
PMID: 20924436; PMCID: PMC2946854.